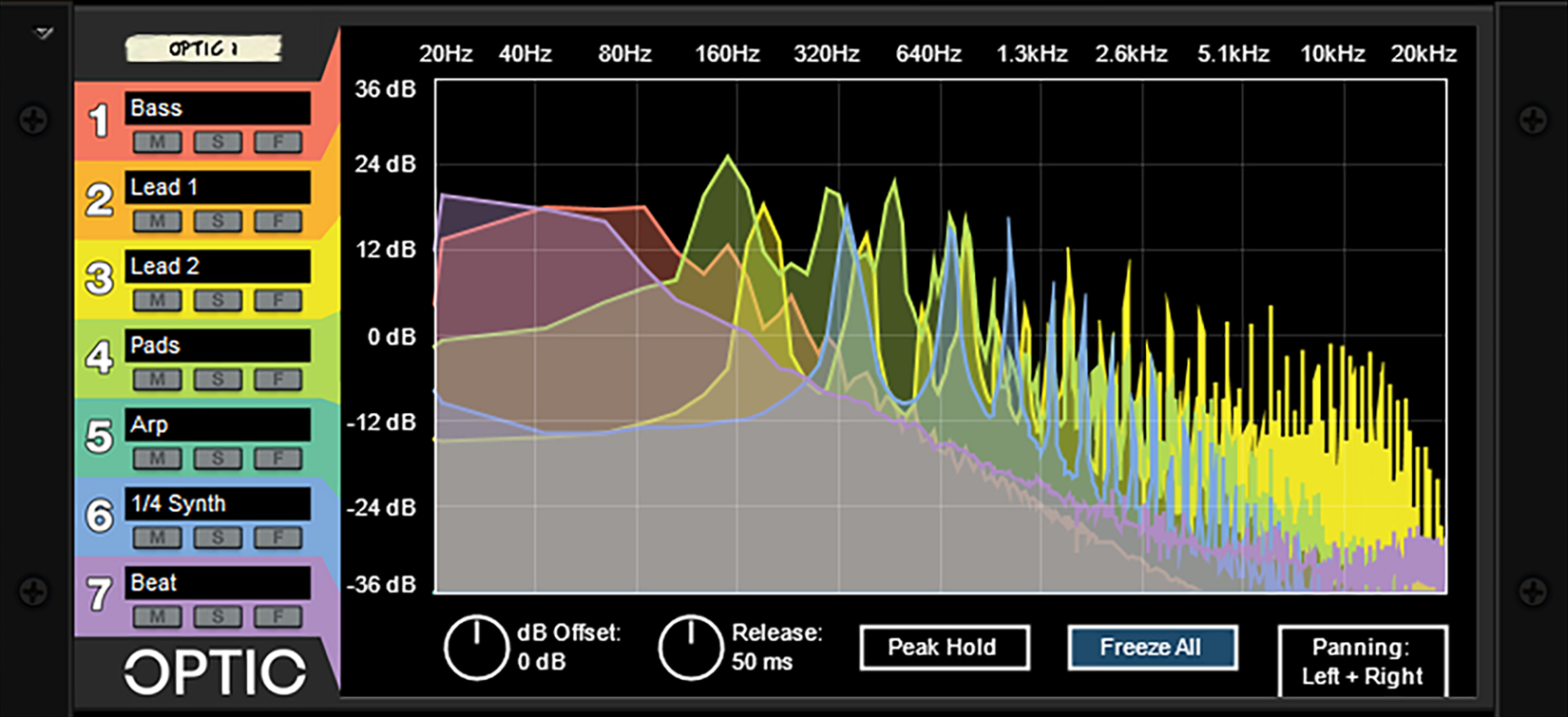
Optic has many powerful uses, such as:
Detecting Frequency Overlap
Reducing frequency overlap between various sound sources in a song will bring clarity to your mix and allow each instrument to stand out in their intended frequency ranges. Using Optic allows the user to visualize these individual sound sources and eliminate overlaps.
Comparing Left and Right Stereo Fields
With support for isolating analysis to just Left or Right panning you can easily compare the stereo fields of your mix, to achieve balance or contrast.
Comparing to Reference
When trying to achieve a specific sound or overall style of mix it is common to make use of a reference. With Optic you can easily compare the frequency content of your sound and the sound you’re trying to achieve to aid in the matching process.
Analyzing a Sound in Stages
You can analyze the same audio source at stages of processing to see how frequency content is altered by various effects and processes. This can lead to greater insight into how a master output bus is coming together or to get a spectral based understanding of certain effects.
- 7 Separate Channels of Frequency Analysis or Oscilloscope
- Mute/Solo/Focus per Channel
- Editable labels per Channel (Front and Back)
- Global dB Offset and Release settings
- Global Peak Hold and Freeze All Modes
- Global Panning Modes
- Multiple Color Schemes (Colorblind Safe Included)
- Audio Passthrough Routing
Please see the video tutorials and manual for information on how to use Optic.
Changelog
1.2.0: Oscilloscope Mode Update (February 2021)
- Added an Oscilloscope Mode to the device
- Analysis Improvements drastically reduce erroneous high frequency spiking
1.1.0: Major Performance Update [Trials Reset] (January 2019)
- Increased Framerate by nearly 400%
- Reduced Onset Delay by 80%
- Added details to Plot Inspector (seen while clicking/dragging)
- Changed default Quality Setting to High
- Release Setting re-scaled
- Behind the scenes improvements and cleanup
1.0.0: Initial Release (11/21/17)